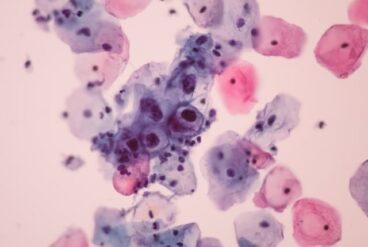
The diagnostic methods we have available are:
Direct identification of infection. HPV DNA is detected using molecular techniques, usually in cells collected from the uterine cervix.
Indirect diagnosis through the discovery of inflammatory lesions caused by HPV. The majority of HPV – induced inflammatory lesions however are not visible to the naked eye in a simple clinical examination (they are subclinical) and diagnosis is indirect when we discover cells inflamed by HPV (in the Pap test) or when inflammatory lesions are found during histological examination of a biopsy (which is usually performed during a colposcopy).